Introduction
- Microservices is a design pattern which is used to develop an entire application by using small independent services.
- Each service has performed specific business logic like payments service, email service, SMS service, order service, document service and communication with other services using an Api and communicating between two microservices using sockets and grpc tool. It will be scaled separately when it’s required to upgrade.
- In simple terms microservices will be divided hole application into the small parts and will excavate based on the requirements , scale, and communicate with each other and provide excepted result to the end user by using entire software.
Why are Microservices Used?
Microservices are used to build flexible, scalable, and easily maintainable applications by dividing them into smaller, independent services.
- Scalable: Each service can scale separately based on its load
- Faster Development: Teams can work and deploy independently.
- Reliable / Fault Isolation: Failure of one service doesn’t affect the whole system.
- Flexible: Different services can use different technologies
- Easy to Maintain: Small, focused services are simpler to update and debug.
When is it Required to Use Microservices?
• We use micro services when the system required continually upgradation, it may complex and larger, multiple teams is working on that that time it will be very helpful.
• Here I’m sharing some key points where we have used the microservices:
- Scalability: To allow each service to scale independently.
- Frequent Updates: If any requires to upgrade with some new logic but do not stop other services of the system.
- Large Development Team: Multiple teams is working on the same project, but their module was different, and it’s become a separate micro service.
- Technology Flexibility:use any tech for to solve the existing problem and
- Cloud and container-based systems: System was deployed on cloud as service for globally using docker Kubernetes for distributed deployment
Advantages of Microservices
There are multiple advantages of MicroServe design patten used in software development and here below key advantages mentioned.
- Scalability: Easier updates without affecting the whole system
- Independent Deployment: Easier updates without affecting the whole system.
- Fault Isolation: You only scale what’s needed, reducing resource waste.
- Faster Development: Each service represents a clear business function.
- Technology Flexibility: Use different languages or frameworks for each service.
- Easier Maintenance: Small, focused codebases are simpler to manage.
- Continuous Delivery: Supports CI/CD and frequent releases.
- Better Performance: Only scale what’s needed, reducing resource waste.
- Improved Reliability: Health checks and load balancing improve uptime.
- Aligned with Business Domains: Each service represents a clear business function.
Create a new solution for microservices demo project and add new two api projects into the base solutions.
Example
Project Name: Microservices Demo
Sub Project1: Service1
Sub Project2: Service2
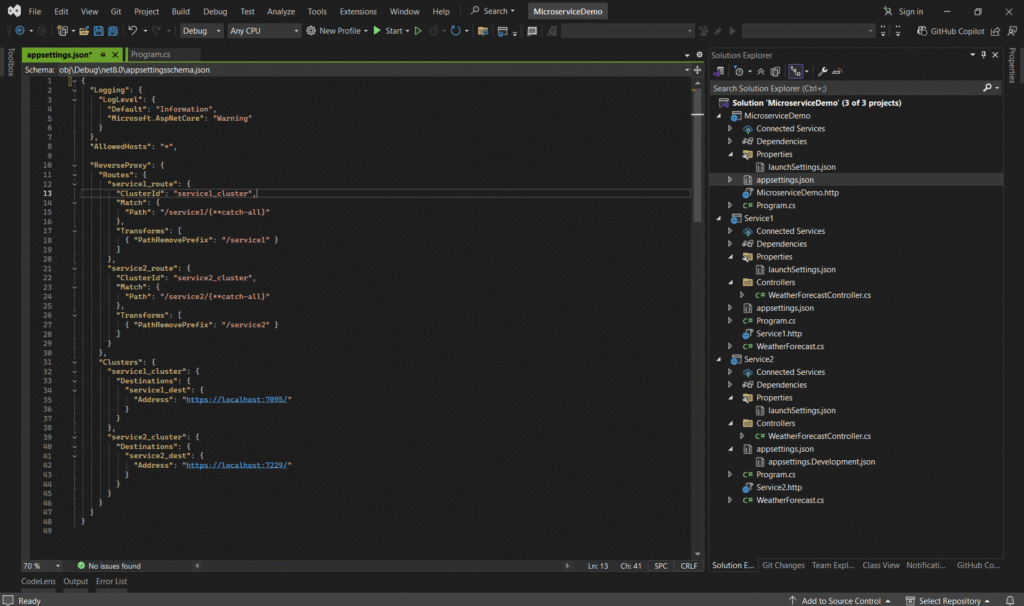
- launchSettings.json controls how each ASP.NET Core project runs locally.
- It defines ports, environment (Development), and startup behavior like Swagger.
- Each microservice (e.g., Service1, Service2) has its own file with unique ports like Service1, Service 2 will be run on localhost:7095 & localhost:7229 on this port receptively.
- Used by Visual Studio or dotnet run to start services independently.
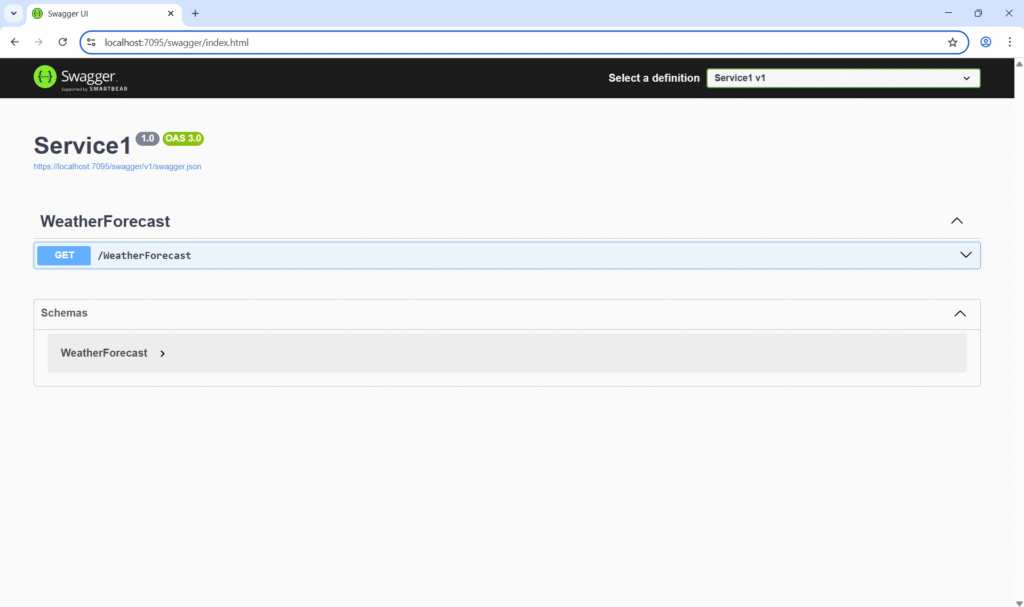
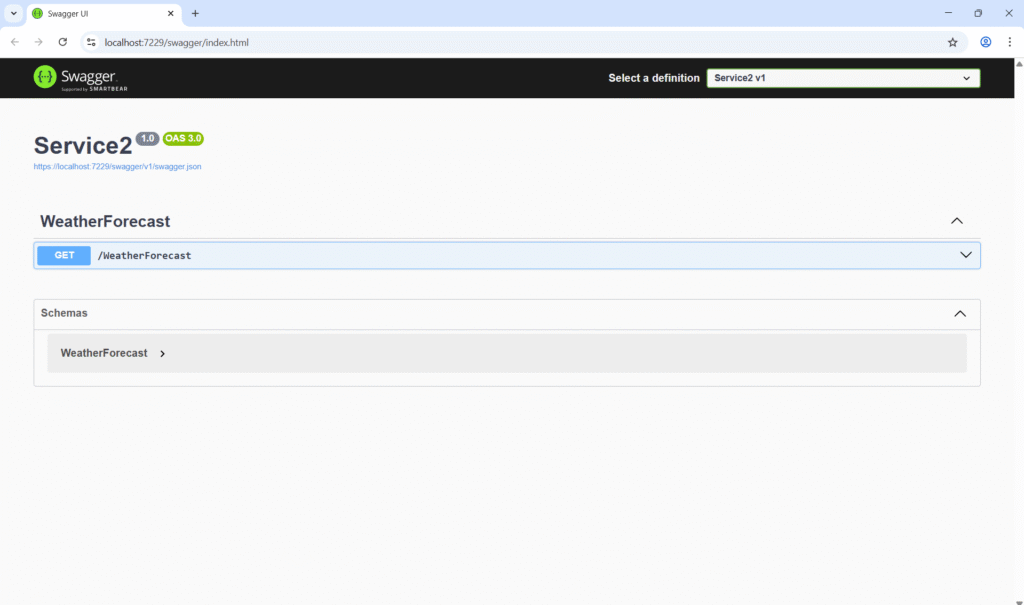
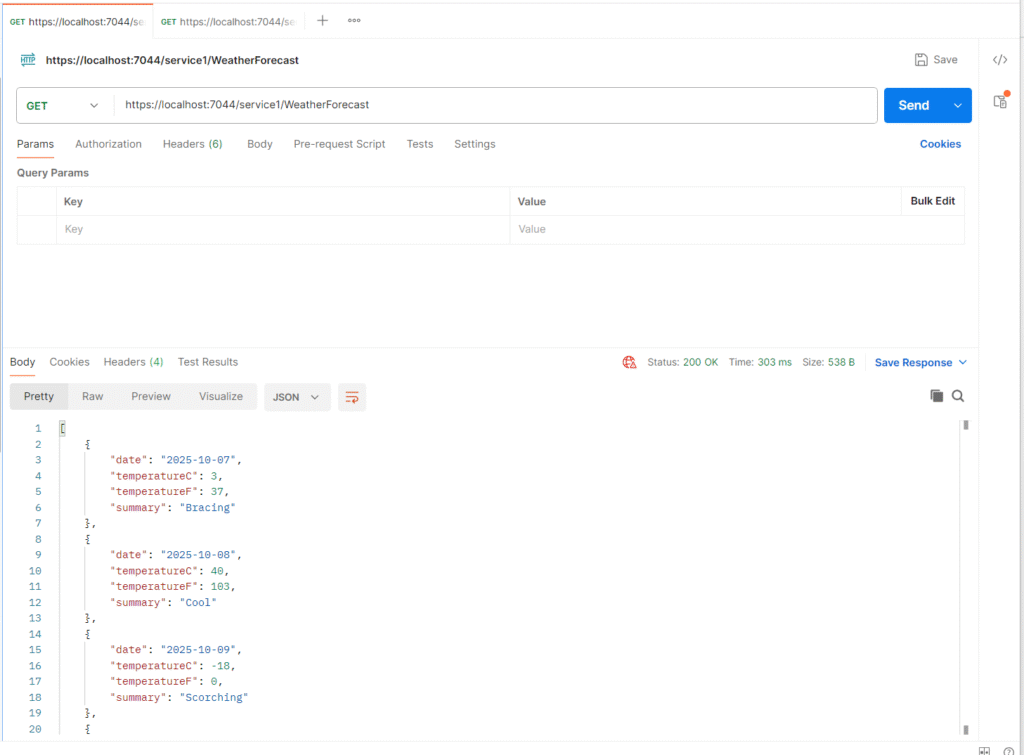
Using a reverse proxy or API Gateway, both can be accessed on a single port like https://localhost:7044/service1 and https://localhost:7044/service2
Disadvantages of Microservices
Here are some key disadvantages and ways to mitigate them:
- Complex Communication: Microservices talk over the network, which increases latency and failure chances. Use an API Gateway, message queues, and service discovery to manage this issue.
- Hard debugging and monitoring: Tracing errors across multiple services is difficult — solve this with centralized logging and distributed tracing tools like ELK, Jaeger, or Grafana.
- Deployment overhead: Managing many services can be complicated — containerize with Docker, orchestrate with Kubernetes, and automate using CI/CD pipelines.
- Data consistency issues: Each service has its own database, making transactions tricky — use event-driven design, saga patterns, and eventual consistency to handle distributed data.
- High setup and learning curve: Setting up infrastructure and training teams takes time — start with a modular monolith, then gradually split, and provide DevOps training.
- Network latency and security risks: More services mean more endpoints and slower calls — use a service mesh (e.g., Istio) for control and secure all APIs with authentication and encryption.
Conclusion
1. Microservices architecture is a modern way to build software by dividing a big application into small, simple, and independent parts. Each part, called a service, does one specific job and talks to other services using APIs.
2. This method makes the system easier to build, test, and update. It also improves speed, flexibility, and reliability, so even if one service fails, the whole system keeps running smoothly.
